Releem: SQL Query Optimization tool for MySQL & MariaDB
As applications evolve, SQL queries tend to change frequently. New queries are introduced, existing ones grow in complexity, and data volume increases. Queries that were fast during development or early production often become slow over time. In many cases, new queries reach production without being tested against real data and workload patterns.
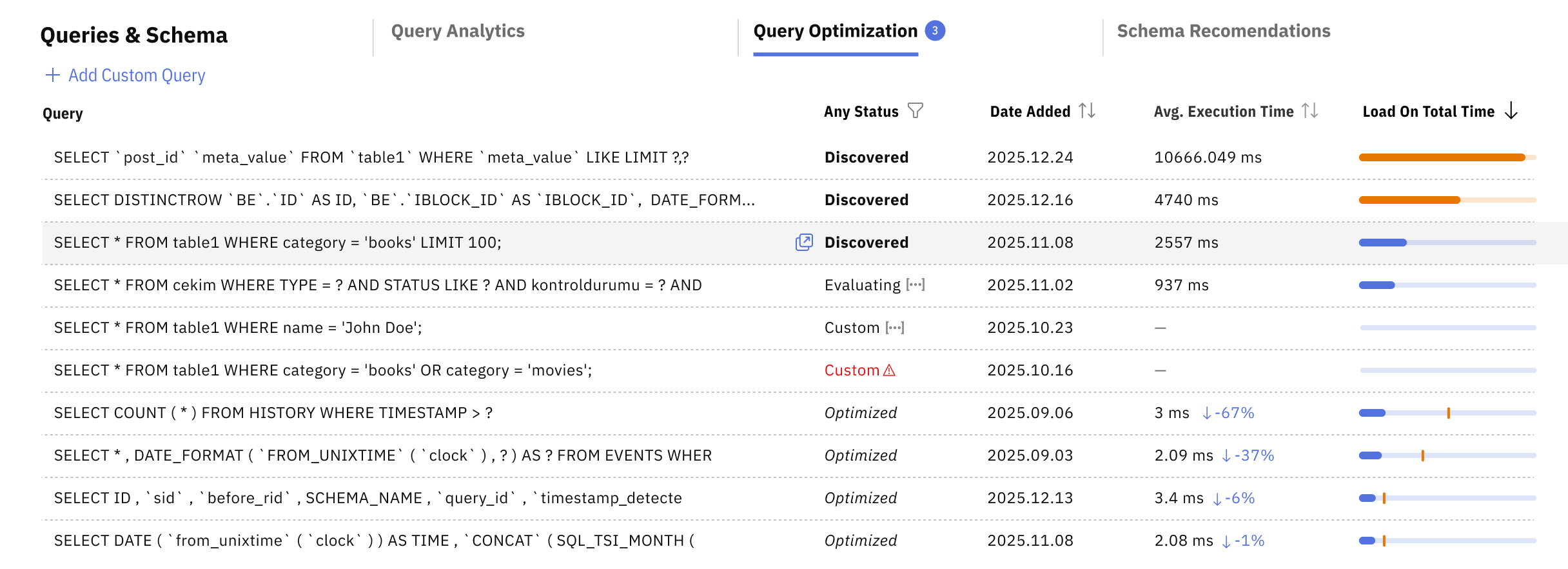
Releem SQL Query Optimization helps identify and improve inefficient queries directly in production. The feature continuously analyzes real query execution data, detects queries with the highest performance impact, and generates actionable optimization recommendations. This allows developers and DBAs to catch performance issues early, understand why a query is slow, and apply safe improvements based on actual usage rather than assumptions.
Releem supports two workflows: automatic weekly analysis of the most impactful queries, and on-demand optimization for any selected query from Query Analytics. In both cases, Releem provides clear recommendations and leaves full control over changes to the engineer.
Releem SQL Query Optimization helps identify and improve inefficient queries directly in production. The feature continuously analyzes real query execution data, detects queries with the highest performance impact, and generates actionable optimization recommendations. This allows developers and DBAs to catch performance issues early, understand why a query is slow, and apply safe improvements based on actual usage rather than assumptions.
Releem supports two workflows: automatic weekly analysis of the most impactful queries, and on-demand optimization for any selected query from Query Analytics. In both cases, Releem provides clear recommendations and leaves full control over changes to the engineer.
How SQL query optimization works
Workflow 1: Automatic weekly query analysis
Releem automatically analyzes production SQL queries once a week to detect performance issues without requiring manual action from engineers.
During each analysis cycle, Releem reviews:
Based on real execution statistics, Releem identifies queries that are inefficient for the current data volume and workload. When an issue is detected, Releem suggests recommendations and marks the query as requiring attention.
This workflow is designed to catch performance regressions early, including queries that became slow over time and new queries that were deployed without being tested under real production conditions.
Releem sent notifications via email and engineers can review recommendations in the dashboard. All changes remain fully under the engineer's control.
During each analysis cycle, Releem reviews:
- The top 100 most frequent queries, which often have the highest cumulative impact on database load
- The top 100 slowest queries, which directly affect application latency
Based on real execution statistics, Releem identifies queries that are inefficient for the current data volume and workload. When an issue is detected, Releem suggests recommendations and marks the query as requiring attention.
This workflow is designed to catch performance regressions early, including queries that became slow over time and new queries that were deployed without being tested under real production conditions.
Releem sent notifications via email and engineers can review recommendations in the dashboard. All changes remain fully under the engineer's control.

Workflow 2: On-demand query optimization
In addition to automatic analysis, Releem allows engineers to request optimization recommendations for any specific query.
From the Query Analytics dashboard, a developer or DBA can select a query and trigger optimization manually. Releem analyzes the selected query using real execution statistics, access patterns, and existing indexes, then generates optimization recommendations tailored to that query.
This workflow is useful when investigating a known performance issue, reviewing a newly deployed query, validating changes before further optimization, debugging slow query log entries.
It provides targeted analysis without waiting for the next automatic cycle, while using the same production data and safety model.
As with automatic optimization, Releem does not apply any changes automatically. All recommendations are presented for review and can be applied manually when appropriate.
From the Query Analytics dashboard, a developer or DBA can select a query and trigger optimization manually. Releem analyzes the selected query using real execution statistics, access patterns, and existing indexes, then generates optimization recommendations tailored to that query.
This workflow is useful when investigating a known performance issue, reviewing a newly deployed query, validating changes before further optimization, debugging slow query log entries.
It provides targeted analysis without waiting for the next automatic cycle, while using the same production data and safety model.
As with automatic optimization, Releem does not apply any changes automatically. All recommendations are presented for review and can be applied manually when appropriate.

Types of query recommendations
Releem analyzes SQL queries at the execution-plan level and classifies issues based on how data is accessed, filtered, joined, and processed in production.
Optimization recommendations focus on improving index usage, reducing unnecessary data processing, optimizing joins, sorting and grouping operations, and correcting schema or index inefficiencies that negatively affect execution plans. In cases where query performance is influenced by server settings, Releem also accounts for configuration-related constraints when suggesting improvements.
Each recommendation is directly tied to observed execution behavior and clearly indicates what can be changed and at which level, whether in query logic, schema, or server configuration.
Optimization recommendations focus on improving index usage, reducing unnecessary data processing, optimizing joins, sorting and grouping operations, and correcting schema or index inefficiencies that negatively affect execution plans. In cases where query performance is influenced by server settings, Releem also accounts for configuration-related constraints when suggesting improvements.
Each recommendation is directly tied to observed execution behavior and clearly indicates what can be changed and at which level, whether in query logic, schema, or server configuration.
Reviewing and applying recommendations
Each optimization recommendation includes a clear explanation of the detected issue and the reasoning behind the proposed change. Recommendations are presented as concrete SQL statements or actionable guidance that can be reviewed in the context of the application and database schema.
Releem does not apply any changes automatically. Engineers review each recommendation, decide when it is appropriate to apply it, and execute the change manually. This ensures that optimizations fit existing deployment processes, change management policies, and production safety requirements.
If a recommendation is not relevant, it can be deleted. Deleted recommendations will not be suggested again in future analysis cycles unless the underlying query or workload changes and a new recommendation is generated. This allows teams to reduce noise and focus only on actionable findings.
Releem does not apply any changes automatically. Engineers review each recommendation, decide when it is appropriate to apply it, and execute the change manually. This ensures that optimizations fit existing deployment processes, change management policies, and production safety requirements.
If a recommendation is not relevant, it can be deleted. Deleted recommendations will not be suggested again in future analysis cycles unless the underlying query or workload changes and a new recommendation is generated. This allows teams to reduce noise and focus only on actionable findings.

Measuring performance improvements
After an optimization recommendation is applied, Releem continues to observe the query using production execution data. This makes it possible to verify whether the change had the intended effect under real workload conditions rather than synthetic benchmarks.
Releem compares query behavior before and after the change, focusing on execution time, frequency, and overall performance impact. This allows engineers to confirm improvements, detect regressions early, and understand the actual effect of each optimization.
By tying recommendations to measurable results, Releem helps teams make incremental, validated improvements to query performance while maintaining confidence in production stability.
Releem compares query behavior before and after the change, focusing on execution time, frequency, and overall performance impact. This allows engineers to confirm improvements, detect regressions early, and understand the actual effect of each optimization.
By tying recommendations to measurable results, Releem helps teams make incremental, validated improvements to query performance while maintaining confidence in production stability.

Releem is more than SQL query optimization tool
Releem is built around the idea that managing MySQL databases should be straightforward. SQL query optimization is one part of a broader advisory system:
- Configuration tuning - Releem analyzes database configuration, workload and system resources, detects inefficient or risky settings, and suggests safe configuration changes to improve performance and stability without manual trial and error.
- Health checks - Releem continuously evaluates key database and system metrics to highlight issues that need attention.
- Schema optimization - Releem checks schema and index structures to detect issues that slow down queries, such as missing or inefficient indexes, and suggests safe improvements without requiring application code changes.
- MySQL monitoring - By tracking workload metrics, Releem identifies performance bottlenecks early, helping you stay ahead of problems without manual investigation.
- Broad compatibility - Releem works with MySQL, MariaDB, Percona Server, and cluster configurations including Percona XtraDB Cluster, Galera Cluster, and InnoDB Cluster. It supports both self-hosted and cloud-managed databases on AWS RDS, Google Cloud SQL, and Azure Database.
Ready to dive in?
Try Releem today for FREE!
Try Releem today for FREE!